A variety of factors can contribute to how and why a company becomes financially distressed. When a business is heading for or arrives in the zone of insolvency, it’s time for management to determine what restructuring options and strategies are available and best suited to maximize asset value.
Should the company proceed informally with an out-of-court restructuring or through an in-court restructuring under Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code? For each distressed company, there are unique legal and business circumstances that will help determine which option is best.
Generally, a consensual restructuring out-of-court can be the most beneficial option. However, a major decision-maker is the company’s liquidity situation. Is there enough liquidity to pursue and negotiate a successful out-of-court restructuring? Read on as we explore each option in greater depth.
Out-of-court restructuring
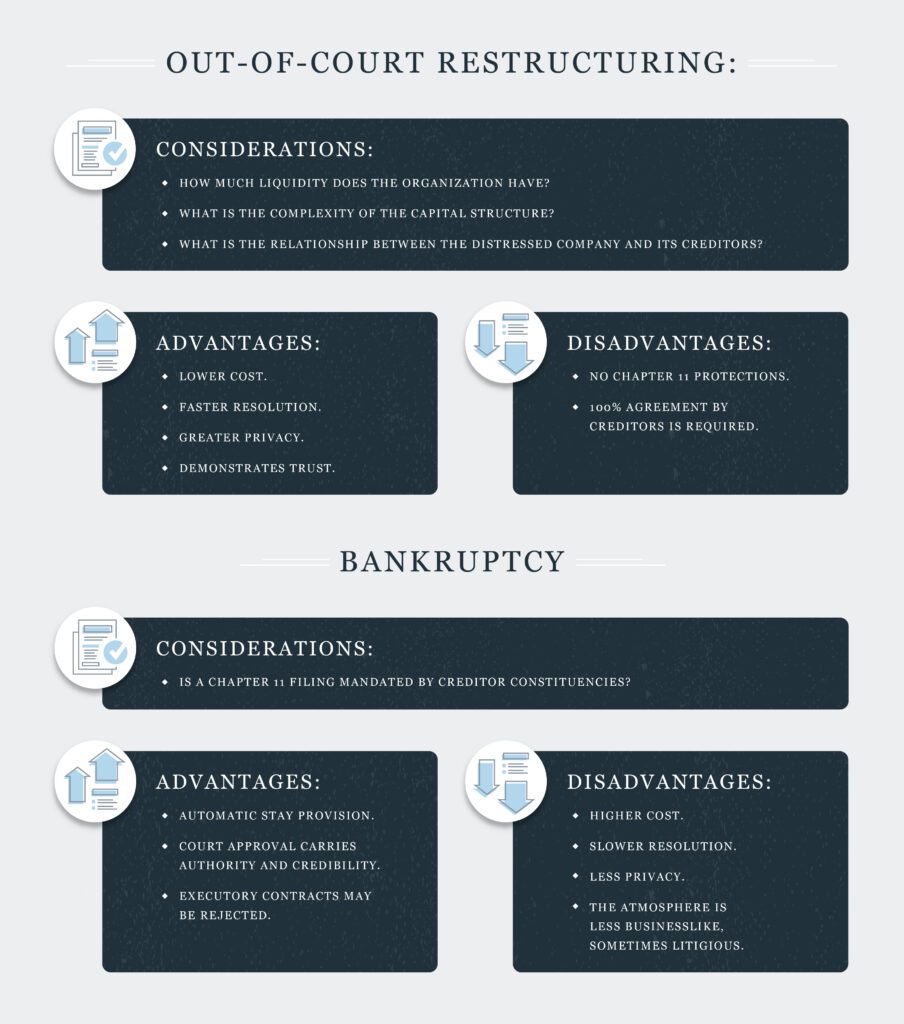
Considerations
How much liquidity does the organization have?
As mentioned previously, a company’s liquidity is a lead indicator of whether out-of-court restructuring is a feasible option. Out-of-court restructuring is a quicker, less expensive choice compared to in-court, which is good if the company has limited cash resources. However, liquidity will ultimately determine if there is enough time to propose and prepare an out-of-court resolution. If the company doesn’t have sufficient liquidity, it will most likely have to begin in-court bankruptcy.
What is the complexity of the capital structure?
If the distressed company has a complicated capital structure, an out-of-court restructuring becomes less viable. As more creditors are involved in the situation, 100% consensus is harder to achieve, and it becomes more likely that at least one of the creditors will oppose the proposal.
However, if the company has a simpler capital structure, the inverse is true: Out-of-court restructuring will become a more viable option. Out-of-court restructuring requires unanimous approval by all creditors (including banks, vendors, trade suppliers and other creditors) to be successful, so the number of claim holders must be manageable.
What is the relationship between the distressed company and its creditors?
For a distressed company to lead a successful out-of-court restructuring, it must reach a financial agreement with all of its significant creditors; all of the company’s lenders, major suppliers and/or any third-party entities involved must agree on the source of the company’s troubles and its potential solutions. This is more likely to happen if the distressed company has a better relationship with all involved parties.
Advantages
Lower cost
A successful out-of-court restructuring is significantly less expensive for the company than a Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceeding. It also gives the distressed company more flexibility to negotiate and propose different strategies to find growth and profit solutions.
Faster resolution
Typically, out-of-court restructuring takes between six to nine months — possibly even less for some companies. Meanwhile, Chapter 11 proceedings average between nine and 12 months, which leads to more time without a resolution for your company.
Greater privacy
Since the out-of-court restructuring process is less bureaucratic compared to in-court proceedings, it has less onerous financial reporting requirements. This means that the process is completed in private without the risks of important financial documents becoming available to the public. This increased privacy also means there’s less business disruption due to public knowledge of financial disputes, which could impact employee morale or trade creditor relationships.
Demonstrates trust
If a distressed company is able to successfully proceed with an out-of-court restructuring, it may signify that creditors have faith and trust in them as a business. Otherwise, creditors would most likely have insisted on the additional protections that are guaranteed through the formal legal process of Chapter 11 proceedings.
Furthermore, agreeing to out-of-court restructuring demonstrates additional confidence in the management team and that any current issues are seen as temporary and repairable by creditors.
Disadvantages
No Chapter 11 protections
The main disadvantages of out-of-court restructuring are the benefits available through in-court Chapter 11 proceedings. With an out-of-court restructuring, companies cannot put a pause on creditors’ demands to pay pre-restructuring obligations and creditors may still proceed with lawsuits.
All creditors must participate
As noted earlier, all relevant parties (including banks, vendors, trade suppliers and other creditors) must be involved and agree unanimously for out-of-court restructuring to succeed. Even if one party dissents, the process is unsuccessful.
Bankruptcy
Considerations
Is in-court restructuring mandated by third parties?
In circumstances where the financial facts show that the distressed company is not viable in its current form, creditors will often opt to work with a company that is engaged in a Chapter 11 process because they can benefit from in-court protections. In this situation, the distressed company may also find that the best solution is a sale. In this case, a Chapter 11 proceeding will be more attractive to the buyer because of its protections and it allows them to buy the company free of any encumbrances or pre-existing claims against the business’s assets.
Advantages
Automatic stay provision
Once the bankruptcy filing is made to the Federal Court, an automatic stay provision goes immediately into effect. This legally prevents creditors from continuing collection efforts, including litigation threats against the distressed business. This largely benefits the distressed company, allowing them to focus on restructuring efforts without further harassment from creditors.
Court approval generates trust
A Chapter 11 proceeding indicates to others that the bankruptcy judge has evaluated all details of the case, giving the distressed company’s plan confidence and approval to emerge from bankruptcy. This approval by the bankruptcy court enables the company to be better positioned to present itself as a viable entity.
Executory contracts rejection
Through a Chapter 11 proceeding, the distressed company can reject or cancel an executory contract that they otherwise wouldn’t be able to leave, including some leases, license agreements, franchise agreements and equipment rental contracts. The total dollar amount of executory rejection can be substantial, especially in retail bankruptcy.
Disadvantages
Higher cost
A Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceeding comes with costly court fees, as well as additional professional and legal fees, that make it significantly more expensive than out-of-court restructuring.
Slower resolution
In-court restructuring takes longer than out-of-court restructuring due to the official bureaucratic processes that are required by federal courts.
Less privacy
In contrast to the privacy of out-of-court restructuring, in-court proceedings require extensive financial reporting requirements, including monthly financial statements and budgets. The distressed company especially loses a big portion of confidentiality due to the advent of new technology, which makes the information more accessible to the public and interested parties.
Less businesslike, more legal
Unlike the informal out-of-court restructuring business process, Chapter 11 proceedings are much more formal as they must be held by a US bankruptcy court. The environment has stringent rules and protocols that must be followed by involved parties.
Conclusion
There are many moving parts and unique factors that will determine whether a distressed company should opt for out-of-court restructuring or in-court restructuring under Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code. However, the common through-line for both processes is that a positive turnaround can be achieved for the distressed company through proactive and strategic decisions.
Both out-of-court and in-court restructuring aims to put the financially distressed company back on the right track and return to sustainable and profitable operations — with no more risk of insolvency. The best choice will vary between each company based on their unique circumstances.
For help in this process, you can reach out to the experts at CFGI for restructuring services.
